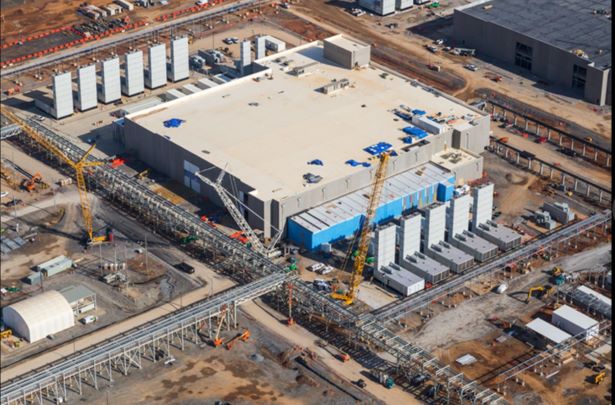

A Green data center may be understood as a repository for the storage, management and dissemination of data in which the mechanical, lighting, electrical and computer systems are designed to maximize energy efficiency and minimize environmental impact. Data centers require a lot of energy to carry out various functions and, thus, greening these would be an important step toward reducing the carbon footprint of a company. A green data center accomplishes this task by employing advanced technologies and strategies.
The various technologies and strategies used in green data centers include reduction of building footprints, low-emission building materials, carpets and paints, sustainable landscaping, e-waste recycling, catalytic converters on backup generators, alternative energy (such as photovoltaic technology, heat pumps and evaporative cooling technology), hybrid or electric vehicles, and so on.
Green data facilities not only help the environment but also add on health benefits by offering employees a healthy and comfortable work environment. Further, due to environmentally friendly practices, Green data centers also enhance relations with local communities.
In addition, to ward off the growing pressure from environmentalists, the companies are seeking ways to reduce energy consumption and sourcing from renewables as much as possible. Energy consumption is one of the highest expenses of a data center. It is also among the top issues that worry data center operators. Green data centers are a viable option to reduce the load in the facilities mostly filled with machines and few people.
In all, Green data centers have several advantages including lower carbon emissions, reduction in waste output, cut down in electricity consumption, promoting the use of renewables, lowering long-term operating costs, and reduction in space requirements.
A Green data facility has characteristic features and components – from how the building is constructed to the equipment in use – which make it sustainable. Design characteristics and components of Green data centers include the following:
Servers are oriented in such a way that enables hot air to be pumped to air conditioner returns and cold air to be pumped where it’s needed for cooling.
The systems use outdoor air to cool data centers and are strategically located in cooler climates.
These servers work well in data centers and their low energy consumption makes them more efficient than traditional servers.
These energy-efficient data centers are portable and can be quickly set up wherever they are needed. They are also called data centers in a box.
Technologies like evaporation pads and high-pressure spray systems, reduce heat through the evaporation of water.
Waste heat from data center power use is reused to heat other facilities.
Energy-efficient ultrasound is used to create the moisture needed to run some devices in a data center.
Several companies have tried to shift their focus on Green data centers and adopted the concept as a part of their sustainable development solutions. The ambitions vary widely in how they plan to reach their targets. While some are taking a long-term industrial approach and providing capital and resources to build a new off-site generation, others are looking to utilize onsite roof space for incremental solar generation. Various others are looking for long-term price certainty and opt for using PPAs from renewable power plants. Some of the biggest cloud services firms , be it Amazon AWS< Google or Microsoft Azure have picked data centres as a critical area for shifting to renewable energy first.
Many of the firms document their renewable energy use with market-based instruments (certificates) like Guarantees of Origin in Europe, RECs in North America and International RECs (I-RECs) in a number of countries in Asia, Latin America and Africa. On the other hand, technology mammoths Facebook, Microsoft, and Google committed to going ‘100% renewable’ through the RE100.
Recently, Vantage Data Centers signed a 20-year PPA with South Africa’s solar energy financing player – SolarAfrica. The investment will back the production of 87MWp of renewable energy and reduce CO2 emissions in the region by 3.8 million tons over the lifetime of the PPA.
Soluna, a leading developer of green data centers for batchable computing, powered by renewable energy, also raised $35M from Spring Lane Capital to Build Green Data Centers, recently.
In India, solar energy is fast emerging as the preferred option to power up data centers for Indian telcos. Last year, Bharti Airtel commissioned a 14-megawatt (MW) captive solar power plant in Uttar Pradesh to meet the energy requirement of data centers in the state. It pans to do the same for all its data centres soon, Reliance Jio Infocomm Ltd also planned to build a solar-powered data center in Uttar Pradesh at an investment of around $950 million. Indian heavyweight Adani Enterprises Ltd also partnered with EdgeConneX, to develop 1 gigawatt (GW) of data centre capacity, powered by renewable energy. EPC major Sterling and Wilson Renewable Energy has also identified the data centre segment as a key opportunity to power with renewable energy solutions.
The curtain raiser for the 2nd edition of the India Bioenergy & Tech Expo (IBETE…
In light of the ongoing debate on whether flue gas desulphurisation (FGD) systems in coal-fired…
In a key step toward advancing clean energy adoption, Ahmedabad headquartered IRM Energy Ltd has…
Biofuels conglomerate Aemetis has announced that its subsidiary in India – Universal Biofuels – has…
The Greater Noida Industrial Development Authority (GNIDA) has commenced construction of a 300-tonne-per-day (TPD) bio-CNG…
The World Earth Day – with this year’s theme on ‘Our Power, Our Planet’ –…