Climate-Related Financial Risks for Banks
The S&P in its latest report titled, ‘Climate Change: Can Banks Weather The Effects?’ has underlined the effect expected of climate change to radically transform the way banks operate and influence the creditworthiness of their products.
S&P Global Ratings sees an accelerated rise in global temperatures, a frequent occurrence of extreme weather events; the direct and indirect effects on businesses; and the likely direct human consequences, such as migration and water scarcity, as factors that financial systems will need to adjust to.
Studies show that the value of global financial assets could drop and losses rise exponentially with the average increase in temperature between 2015 and 2100. Understanding the main climate change risks for the banking industry is therefore of ‘paramount importance’ for banks to minimize future climate-related costs and the impact on their creditworthiness.

[related_post]
According to this, some lenders will be better equipped to handle this as they take action to align their businesses and portfolio according to the low carbon transition. “Companies that take a long time to adjust to the low-carbon transition could experience a decline in creditworthiness, which could weaken the asset quality of banks’ lending to them or invest in their debt instruments,” said S&P.
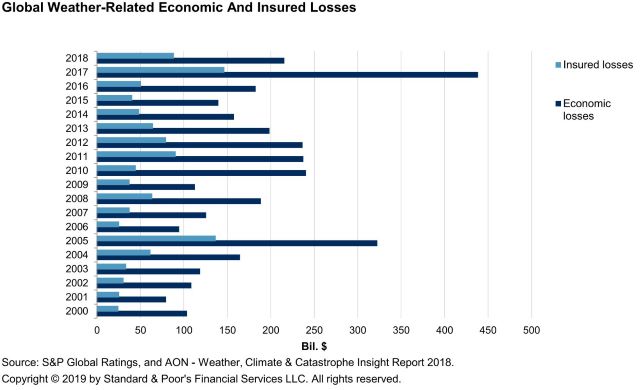
According to the Network for Greening the Financing System (NGFS), the number of extreme weather events has more than tripled since 1980, while worldwide economic costs from natural disasters have exceeded the 30-year average of $140 billion per annum over the past eight years.
With non-life insurance coverage representing less than 10% of GDP, even in developed countries, the proportion of uninsured losses from such events falls directly on households and on companies’ balance sheets. This could lead to a significant increase in credit risk for banks stemming from decreased debt-repayment capacity, impaired collateral values, and higher lending costs.
The report adds that severe weather events could also stunt economic growth, hamper employment, and weaken national infrastructure.
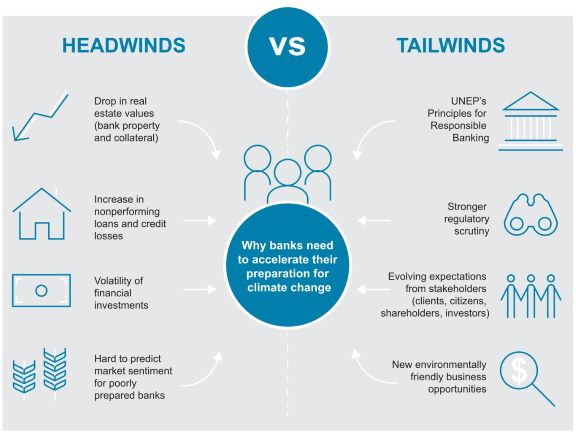
This is why, the report observes, most banks are increasingly embedding climate change risks in their strategic planning. In addition, albeit still work in progress, their risk appetite frameworks are also changing, and we see banks gradually reducing exposure to environment unfriendly sectors. Green financing has taken off over the past five years, For example, S&P expects the global green-bond-labeled market to expand by a healthy 8% in 2019 to a record $180 billion in absolute terms, despite slowing debt markets.
To read the report in detail, click here
In a significant move toward advancing green energy and industrial growth in the state, Himachal…
Golabl chemical conglomerate BASF has announced that its now offering the world’s first biomass-balanced polyethersulfone…
In a crucial stint to bolster the biogas sector and sustainable dairying in the country,…
TotalEnergies SE has received approval to proceed with its Middlebrook solar and battery project in…
Andhra Pradesh Chief Minister Chandrababu Naidu has inaugurated the Rs 1,000-crore green hydrogen plant of…
The BITS Pilani has developed an innovative solution for managing landfill leachate, domestic septage, and…