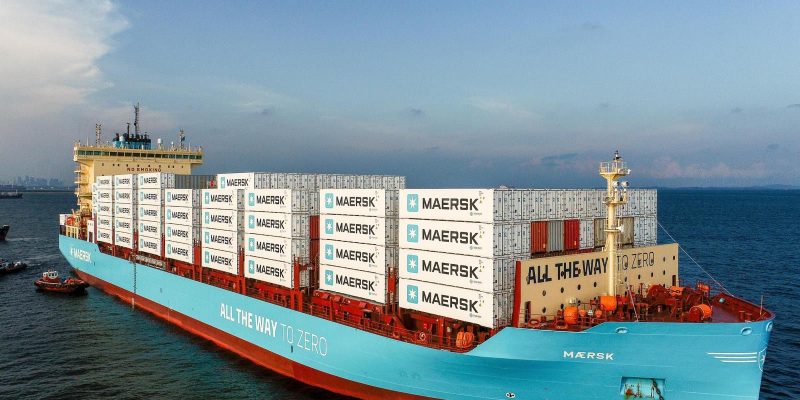

The world’s largest methanol-enabled container vessel has been unveiled and named by Maersk “Ane Maersk” at a ceremony in the shipyard of HD Hyundai Heavy Industries (HD HHI) in Ulsan, South Korea.
The vessel is named after Ane Maersk Mc-Kinney Uggla, the Chair of the A.P. Moller Foundation and A.P. Moller Holding. Ane’s eldest granddaughter served as godmother and christened the vessel by breaking a champagne bottle over the bow.
“Ane Maersk” is the first of Maersk’s 18 large methanol-enabled vessels, that will be delivered between 2024 and 2025. It is the world’s second methanol-enabled container vessel. In the beginning of February, it will enter service on the AE7 string connecting Asia and Europe, marking a significant milestone in the company’s commitment to pioneering low-emissions shipping solutions. The vessels in the new series have an industry-first innovative design with the bridge and accommodation placed at the very front of the vessel, which ensures fuel efficient operations.
Vincent Clerc, CEO, AP Moller-Maersk, said, “This series of vessels will have a transformative impact on our ambition to progress on our industry-leading climate ambitions. It is a visual and operational proof of our commitment to a more sustainable industry. With “Ane Maersk” and her sister vessels we are expanding our offer to the growing number of businesses aiming to reduce emissions from their supply chains.”
“Ane Maersk” will begin her maiden voyage on green1 methanol and Maersk continues to work diligently on 2024-2025 sourcing and bunkering solutions for its methanol-enabled vessel fleet.
Maersk defines“green fuels” as fuels with low to very low GHG emissions over their life cycle compared to fossil fuels. Different green fuels achieve different life cycle reductions depending on their production pathway. By ‘low’ we refer to fuels with 65-80% life cycle GHG reductions compared to fossil fuels. This covers, e.g., some biodiesels. ”Very low” refers to fuels with 80-95% life cycle GHG reductions compared to fossil fuels.
1. The mandate for blending Compressed Biogas (CBG) with natural gas has come into effect…
Andhra Pradesh is striving towards greening its energy sector with quite some speed. In a…
With an objective to bolster India’s green energy goals, a Tripartite Agreement has been signed…
The Union MNRE Minister Pralhad Joshi launched the Green Hydrogen Certification Scheme of India (GHCI)…
India’s energy conglomerate Bharat Petroleum Corporation Limited (BPCL) has commissioned a 5MW green hydrogen plant…
In a historical development, the European Space Agency (ESA) has successfully launched its pioneering ‘Biomass’…