Green Hydrogen Use Can Reduce Shipping Sector Emissions By 7.5% Till 2030–31: TERI
The TERI report holds that the adoption of LNG and green ammonia under the Transition to Green Shipping scenario is expected to reduce GHG emissions (well-to-wake) by 7.5% in 2030–31 compared to the baseline scenario.
 Green Hydrogen Use Can Reduce Shipping Sector Emissions By 7.5% Till 2030–31: TERI
Green Hydrogen Use Can Reduce Shipping Sector Emissions By 7.5% Till 2030–31: TERI
The government has initiated the use of green hydrogen to decarbonize the transportation sector, which contributes 5% of the gross value added (GVA). The Green hydrogen use in the transport sector could help replace diesel through initiatives as detailed in a recent TERI report titled “Roadmap for India’s Energy Transition in the Transport Sector.”
The government recently introduced a series of measures, including supporting the use of hydrogen and liquified natural gas (LNG) as alternative fuels.
Snapshot: Coastal Shipping
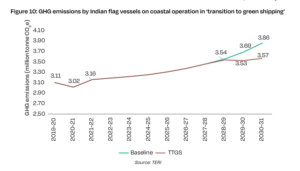
TERI report says that with increasing economic activity, coastal cargo traffic is projected to grow 1.7 times by 2030–31 compared to 2021–22. In Indian coastal shipping, LNG and derivatives of green hydrogen, such as green ammonia and green methanol, are anticipated to play key roles in decarbonization. The adoption of LNG and green ammonia under the Transition to Green Shipping (TTGS) scenario is expected to reduce GHG emissions (well-to-wake) by 7.5% in 2030–31 compared to the baseline scenario.
The emphasis moving forward is expected to shift toward derivatives of green hydrogen, while LNG serves as a transition fuel due to its relatively high GHG emissions over its complete lifecycle.
Adoption Path: Hydrogen as Fuel
In the transportation sector, the adoption of hydrogen as a fuel is likely to follow a phased across grey hydrogen, blue hydrogen, green hydrogen. The report suggested the path of leveraging its lower production cost in grey hydrogen, supports the transition to blue hydrogen in the medium term and a gradual shift to green hydrogen as production costs decline in the long run. These steps are to ensure green hydrogen supply chain security, international collaboration to source fuel and critical minerals for fuel cells, most of which are currently imported.
The TERI report explores the potential of green hydrogen in the transportation segment, particularly since the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) in the medium and heavy goods vehicle (MHGV) sector remains low in India.
In addition to promoting the electrification of this segment, the report emphasizes the exploration of hydrogen and LNG as alternative fuels to replace diesel. A noteworthy initiative in this regard is the National Green Hydrogen Mission, launched in 2023. The report perceives
Currently, the production cost of green hydrogen is significantly higher than that of grey or blue hydrogen. However, a cost-effective yet cleaner form of hydrogen can provide India with greenhouse gas (GHG) emission abatement at a reasonable cost before transitioning fully to green hydrogen when it becomes economically viable.
India is also expected to expand its biofuel blending with petrol, diesel, compressed natural gas (CNG), and aviation turbine fuel (ATF). The updated National Policy on Biofuels has set the following targets. By 2025, India has targeted to increase ethanol blending to 20% with petrol by 2025, reach the target of 5% biodiesel blending with diesel by 2030, achieve 5% compressed biogas (CBG) blending obligation with CNG by 2028–29. Whereas, India expects 2% sustainable aviation fuel (SAF) blending for international flights by 2028.
Expected Result From Ethanol Blending
Almost five-fold increase in estimated number of on-road vehicles between 2019–20 and 2070–71 (204 million in 2019–20, 474 million
in 2030–31, 847 million in 2050–51, and 966 million in 2070-71), however, the dominance of two-wheelers (2W) will weaken due to larger adoption of four-wheelers (4W) in India. Thus, a shift from modes with less GHG footprint per PKM (2W and Bus) to four-wheelers can observed, and by 2070–71 it is expected that the modal share of 4W will be more than the combined modal shares of Bus and 2W (31 percent) according to Teri report findings.




