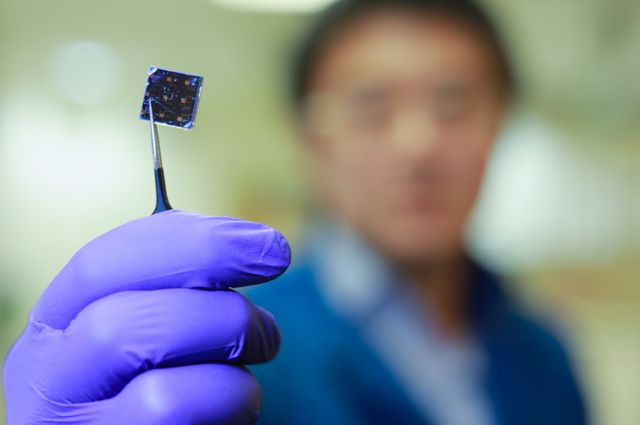
Scientists from UCLA have developed a highly efficient thin-film solar cell using a double-layered design, which generates more energy from sunlight than any previous model using the perovskite–CIGS tandem solar cell technology. The latest improvement builds on previous hopes from Perovskite cells.


The research led by, UCLA’s Professor of Materials Science Yang Yang and his team at the Samuell School of Engineering created a new cell that converts 22.4 percent of the incoming energy from the sun, a record in power conversion efficiency for a perovskite–CIGS tandem solar cell. The performance was confirmed by tests at the U.S. Department of Energy’s National Renewable Energy Laboratory. Beating the previous record of 10.9 percent, set at IBM’s Thomas J. Watson Research Center. The device’s efficiency rate is similar to that of the poly-silicon solar cells that currently dominate the photovoltaics market.
The device was made by spraying a thin layer of perovskite, an inexpensive compound of lead and iodine, onto a commercially available solar cell. The solar cell that forms the bottom layer of the device is made of a compound of copper, indium, gallium and selenide, or CIGS.
“With our tandem solar cell design, we’re drawing energy from two distinct parts of the solar spectrum over the same device area,” Yang said. “This increases the amount of energy generated from sunlight compared to the CIGS layer alone.” According to him, this technique of spraying on a layer of perovskite could be easily and inexpensively incorporated into existing solar-cell manufacturing processes.
The cell’s CIGS base layer, which is about 2 microns (or two-thousandths of a millimetre) thick, absorbs sunlight and generates energy at a rate of 18.7 percent efficiency on its own, but adding the 1 micron-thick perovskite layer according to the team, improves its efficiency. The two layers are joined by a nanoscale interface that the UCLA researchers designed; the interface helps give the device higher voltage, which increases the amount of power it can export.
“Our technology boosted the existing CIGS solar cell performance by nearly 20 percent from its original performance,” Yang said. “That means a 20 percent reduction in energy costs.” He added that devices using the two-layer design could eventually approach 30 percent power conversion efficiency. That will be the research group’s next goal.
Image Credits: Oszie Tarula/UCLA
Read our report on a solar screen that can bend and roll.
1. The mandate for blending Compressed Biogas (CBG) with natural gas has come into effect…
Andhra Pradesh is striving towards greening its energy sector with quite some speed. In a…
With an objective to bolster India’s green energy goals, a Tripartite Agreement has been signed…
The Union MNRE Minister Pralhad Joshi launched the Green Hydrogen Certification Scheme of India (GHCI)…
India’s energy conglomerate Bharat Petroleum Corporation Limited (BPCL) has commissioned a 5MW green hydrogen plant…
In a historical development, the European Space Agency (ESA) has successfully launched its pioneering ‘Biomass’…