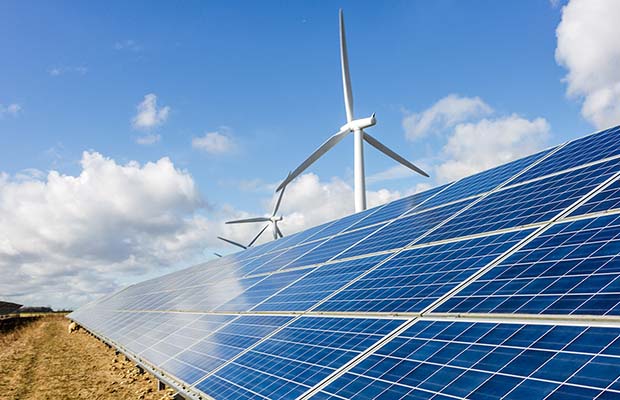

A team of scientist from Stanford University have outlined new steps that 143 countries around the world can take to attain 100 percent clean, renewable energy by the year 2050. The roadmap, published in the journal One Earth, uses the latest energy data available in each country to offer more precise guidance on how to reach those commitments.
It comes ten years after the publication by scientists of the first plan for powering the world with wind, water, and solar.
Mark Z. Jacobson from Stanford University and his team focussed on low-cost, stable grid solutions in 24 world regions encompassing the 143 countries. They project that transitioning to clean, renewable energy could reduce worldwide energy needs by 57 percent, create 28.6 million more jobs than are lost, and reduce energy, health, and climate costs by 91 percent compared with a business-as-usual analysis.
The new roadmap makes use of updated data about how each country’s energy use is changing, acknowledges lower costs and greater availability of renewable energy and storage technology. It includes new countries in its analysis and accounts for recently built clean, renewable infrastructure in some countries.
“There are a lot of countries that have committed to doing something to counteract the growing impacts of global warming, but they still don’t know exactly what to do,” said Jacobson.
The roadmap calls for the electrification of all energy sectors, for increased energy efficiency leading to reduced energy use, and for the development of wind, water, and solar infrastructure that can supply 80 percent of all power by 2030 and 100 percent of all power by 2050.
The new model suggests that the efficiency of electric and hydrogen fuel cell vehicles over fossil fuel vehicles, of the electrified industry over the fossil industry, could substantially decrease overall energy use. The efficiency of electric heat pumps over fossil heating and cooling, along with the elimination of energy needed for mining, transporting, and refining fossil fuels will have the same effects.
The transition to wind, water, and solar would require an initial investment of USD 73 trillion worldwide, but this would pay for itself over time by energy sales, the researchers said. In addition, clean, renewable energy is cheaper to generate over time than are fossil fuels, so the investment reduces annual energy costs significantly, they added.
It reduces air pollution and its health impacts, and only requires 0.17 percent of the 143 countries’ total land area for new infrastructure and 0.48 percent of their total land area for spacing purposes, such as between wind turbines, according to the researchers.
Source: Saurenergy.com
1. The mandate for blending Compressed Biogas (CBG) with natural gas has come into effect…
Andhra Pradesh is striving towards greening its energy sector with quite some speed. In a…
With an objective to bolster India’s green energy goals, a Tripartite Agreement has been signed…
The Union MNRE Minister Pralhad Joshi launched the Green Hydrogen Certification Scheme of India (GHCI)…
India’s energy conglomerate Bharat Petroleum Corporation Limited (BPCL) has commissioned a 5MW green hydrogen plant…
In a historical development, the European Space Agency (ESA) has successfully launched its pioneering ‘Biomass’…