
The Massive Earth Foundation, focused on finding solutions to the pressing environment problems of today, has come out with early findings of its research on AQI (Air Quality Index) data for 8 cities across India. The foundation looked at data for the 8 cities , spread across 12 days, for 4 years. Most of the data was sourced from the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB). In some ways, the lockdown has also offered the best possible opportunity to measure baseline pollution levels in these cities, helping get a fix on the absolute best case scenarios to benchmark with in the future,

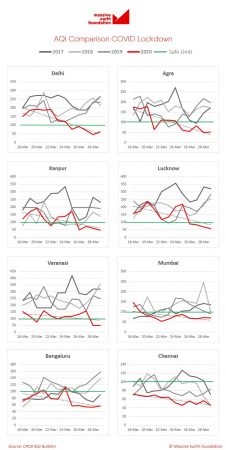
With an assumption of zero vehicular movement and industrial activity, the data offers some interesting on the situation. The authors note that a key factor that has not changed is the high share of fossil fuel powered energy in the overall energy mix.
The drop is far sharper in North Indian cities that have featured in the world’s most polluted lists regularly till date, as compared to cities lower down the map of India, like Mumbai, Bengaluru, Chennai.
With Delhi and Bengaluru clocking almost similar AQI levels, the study wonders if climatic conditions and latitude don’t really have an impact. The similarities between the two doesn’t stop at the almost same AQI. It goes on to highlight that both cities have been plagued with a high vehicular population and movement, score high on construction activity, and remain land locked. Thus, it posts that the difference in 2017-19 could possibly be due to Delhi’s much higher vehicles population. The average difference in AQI (for same period) is 150 in 2017, 100 in 2018 & 60 in 2019.
The foundation will be expanding the study to a larger number of cities soon.
While this is a good start, one hopes that many other institutes are able to mobilise enough resources and their teams to do more detailed studies on the environmental impact of the lockdown. As of now, raw data from multiple sources, on reduced untreated effluent flow to key rivers for instance, or wastewater generation, or even overall water consumption, indicates that it is a big net positive for the environment at least.
With actual electricity demand expected to have dropped by almost 25 percent, we don’t have data yet on the backdown of base load thermal power stations yet. That should become available by early April. In local catchment areas, even those closures could help get a fix on the impact from such power stations on local AQI levels, for instance.
In a significant move toward advancing green energy and industrial growth in the state, Himachal…
Golabl chemical conglomerate BASF has announced that its now offering the world’s first biomass-balanced polyethersulfone…
In a crucial stint to bolster the biogas sector and sustainable dairying in the country,…
TotalEnergies SE has received approval to proceed with its Middlebrook solar and battery project in…
Andhra Pradesh Chief Minister Chandrababu Naidu has inaugurated the Rs 1,000-crore green hydrogen plant of…
The BITS Pilani has developed an innovative solution for managing landfill leachate, domestic septage, and…