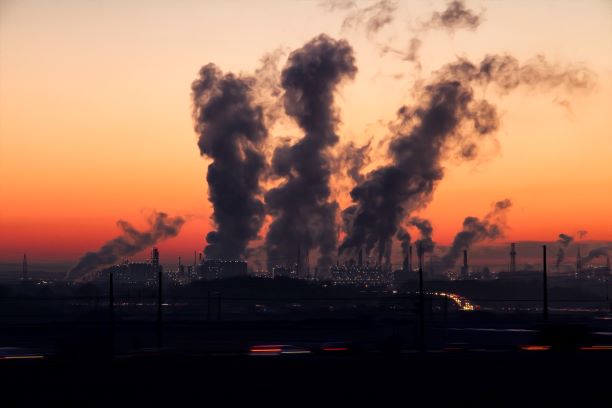

A new study by Nomura Research has concluded that construction of compressed biogas (CBG) plants has the potential to reduce Delhi’s winter pollution by approximately 30 per cent. The study held that CBG projects would be based on utilizing paddy straw as a key feedstock.
Nomura Research highlights that a single CBG plant can mitigate emissions equivalent to those of 150,000 electric cars. The study notes, “Vehicles contribute 20-30 per cent to Delhi’s particulate matter (PM) emissions, with older vehicles being the primary contributors, while newer BS-6 compliant vehicles have a minimal impact. For instance, the BS-6 compliant cars introduced each year account for only 0.2 per cent of Delhi’s pollution.”
Delhi’s severe air pollution stems from multiple sources, including vehicular emissions, construction dust, biomass burning and industrial pollution. Nomura Research mentions that vehicles contribute 20 per cent to the city’s pollution in summer and stubble burning 16 per cent but these figures rise to 30 per cent and 23 per cent, respectively, in winter season. “During peak stubble-burning season, biomass-burning emissions frequently exceed 30 per cent,” the study notes.
Many studies have held that India possesses abundant feedstocks for CBG production, including paddy straw, press mud, municipal solid waste, cow dung, and chicken litter. “Among these, paddy straw is the most promising due to its high CBG yield (11 per cent) and widespread availability. Punjab and Haryana alone produce nearly 12 per cent of India’s surplus agricultural residues, making them ideal for large-scale CBG expansion. Given these advantages, CBG can play a crucial role in reducing Delhi’s air pollution. For example, a CBG plant generating 10 tons of CBG daily requires 90 tons of paddy straw,” the study states.
Starting in 2025-26, the Union petroleum ministry will mandate CBG blending, requiring city gas distribution (CGD) entities to procure and distribute CBG under the CBG-CGD synchronization scheme. The blending targets are set at one per cent in FY26, three per cent in FY27, four per cent in FY28, and five per cent from FY29 onward. However, no penalties have been outlined for non-compliance.
1. The mandate for blending Compressed Biogas (CBG) with natural gas has come into effect…
Andhra Pradesh is striving towards greening its energy sector with quite some speed. In a…
With an objective to bolster India’s green energy goals, a Tripartite Agreement has been signed…
The Union MNRE Minister Pralhad Joshi launched the Green Hydrogen Certification Scheme of India (GHCI)…
India’s energy conglomerate Bharat Petroleum Corporation Limited (BPCL) has commissioned a 5MW green hydrogen plant…
In a historical development, the European Space Agency (ESA) has successfully launched its pioneering ‘Biomass’…